2. Build Controller Host¶
This page is based on the following OpenStack Installation Guide pages:
http://docs.openstack.org/liberty/install-guide-rdo/environment-networking-controller.html
http://docs.openstack.org/liberty/install-guide-rdo/environment-ntp-controller.html
http://docs.openstack.org/liberty/install-guide-rdo/environment-packages.html
- In this guide, I am using a Virtual Machine running on a VMWare hypervisor as my control node. If you are doing the same, you must ensure that the vSwitches on the hypervisor have “promiscuous mode” enabled.
- Boot the control node with the CentOS 7.2.1511 DVD.
- Set your time zone and language.
- For “Software Selection”, set this to “
Infrastructure Server”. - Keep automatic partitioning. Allow to install only on first disk.
- Set the controller’s IPv4 address and hostname. Disable IPv6. Give the connection the name “eth1”.
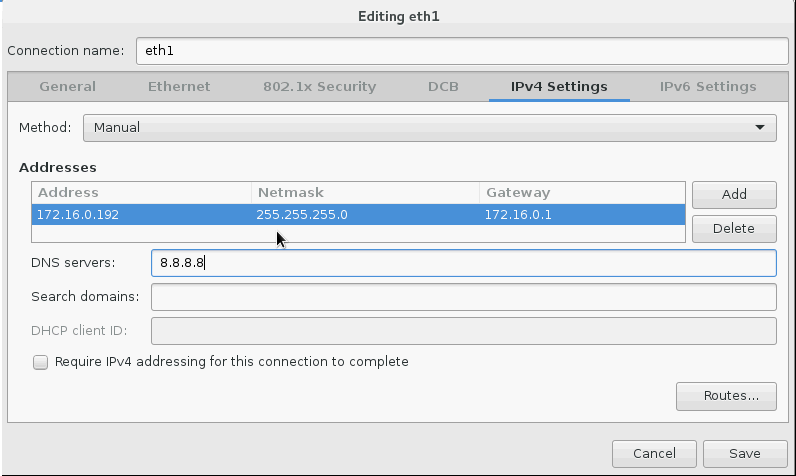
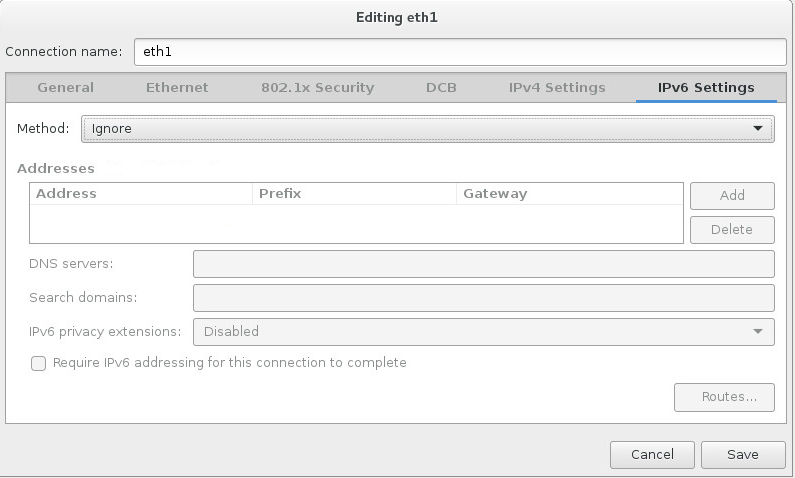
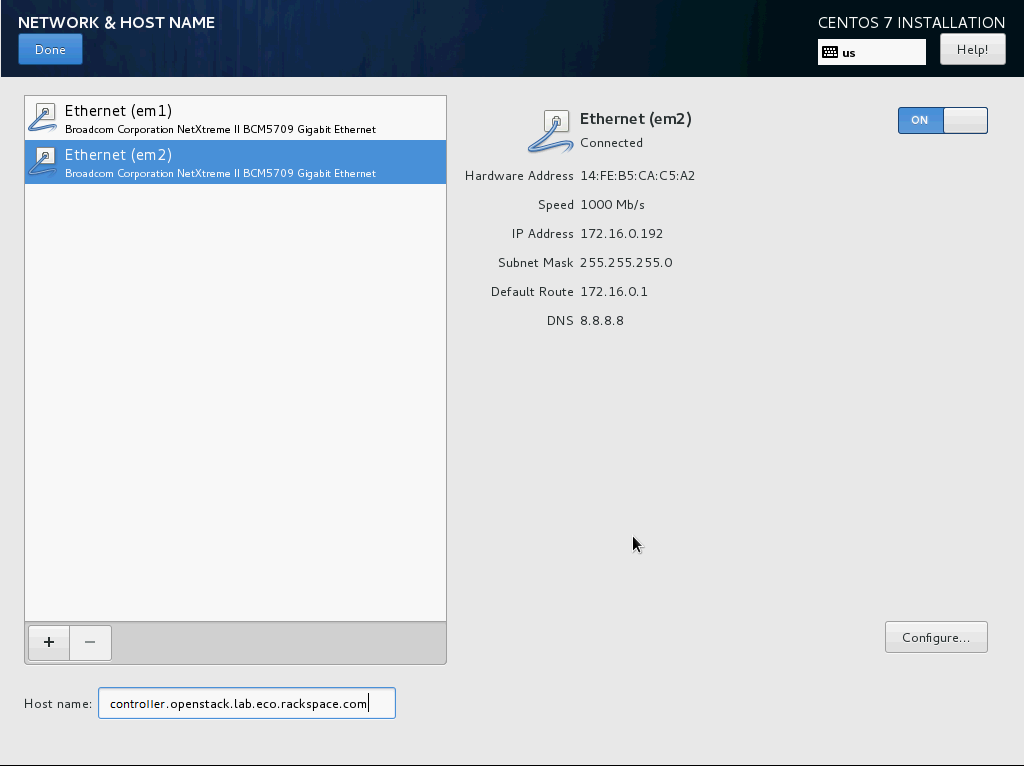
Click on “Begin Installation”.
Set a good root password.
Once installation is complete, reboot the server, and remove the DVD/ISO from the server.
SSH in to server as root.
Stop and disable the firewalld service:
# systemctl disable firewalld.service # systemctl stop firewalld.service
Disable SELINUX:
# setenforce 0 # vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux SELINUX=permissive
Update all packages on the server:
# yum update
If running the control node on VMWare, install the VM tools:
# yum install open-vm-tools
We need persistent network interface names, so we’ll configure udev to give us these. Replace
00:00:00:00:00:00with the MAC addresses of your control node:# vim /etc/udev/rules.d/90-persistent-net.rules SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*",ATTR{address}=="00:00:00:00:00:00",ATTR{dev_id}=="0x0", ATTR{type}=="1",KERNEL=="eno*", NAME="eth0" SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*",ATTR{address}=="00:00:00:00:00:00",ATTR{dev_id}=="0x0", ATTR{type}=="1",KERNEL=="eno*", NAME="eth1"
- Note: This file is case-sensitive, and the MAC addresses should be lower-case.
Rename the network interface configuration files to eth0 and eth1. Replace
eno00000001andeno00000002with the names of your control node’s interfaces:# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts # mv ifcfg-eno00000001 ifcfg-eth0 # mv ifcfg-eno00000002 ifcfg-eth1
Modify the interface configuration files, replacing any instances of
eno00000001andeno00000002(or whatever your interface names are) witheth0andeth1respectively:# vim ifcfg-eth0 NAME=eth0 DEVICE=eth0 # vim ifcfg-eth1 NAME=eth1 DEVICE=eth1
Reboot the control node:
# systemctl reboot
SSH back in as root after the reboot.
Check that ifconfig now shows
eth0andeth1:# ifconfig eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 ether 00:0c:29:d9:36:46 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 172313 bytes 34438137 (32.8 MiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 7298 bytes 1552292 (1.4 MiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 eth1: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 172.16.0.192 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 172.16.0.255 inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fed9:3650 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether 00:0c:29:d9:36:50 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 1487929 bytes 210511596 (200.7 MiB) RX errors 0 dropped 11 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 781276 bytes 4320203416 (4.0 GiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536 inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0 inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host> loop txqueuelen 0 (Local Loopback) RX packets 2462286 bytes 3417529317 (3.1 GiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 2462286 bytes 3417529317 (3.1 GiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0Update the system hosts file with entries for all nodes:
# vim /etc/hosts 172.16.0.192 controller controller.openstack.lab.eco.rackspace.com 172.16.0.203 compute1 compute1.openstack.lab.eco.rackspace.com 172.16.0.204 compute1-vm compute1-vm.openstack.lab.eco.rackspace.com 172.16.0.195 compute2 compute2.openstack.lab.eco.rackspace.com 172.16.0.196 block1 block1.openstack.lab.eco.rackspace.com 172.16.0.197 object1 object1.openstack.lab.eco.rackspace.com 172.16.0.198 object2 object2.openstack.lab.eco.rackspace.com
Update the “Chrony” (NTP Server) configuration to allow connections from our other nodes:
# vim /etc/chrony.conf Allow 172.16.0.0/24
Restart the Chrony service:
# systemctl restart chronyd.service
Enable the OpenStack-Liberty yum repository:
# yum install centos-release-openstack-liberty
Install the OpenStack client and SELINUX support:
# yum install python-openstackclient openstack-selinux